Latest Version
4.20.13
December 12, 2024
TP-LINK SYSTEMS INC.
Tools
Android
0
Free
com.tplink.omada
Report a Problem
More About TP-Link Omada
Understanding Standalone and Controller Modes for EAP Management
In the realm of network management, particularly for EAPs (Enterprise Access Points) and wireless routers, understanding the operational modes is crucial for optimizing performance and functionality. This article delves into the two primary modes: Standalone Mode and Controller Mode, highlighting their features, benefits, and compatibility.
What is Standalone Mode?
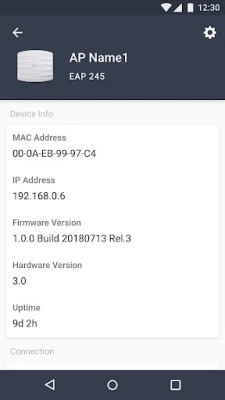
Standalone Mode is tailored for users who need to manage EAPs or wireless routers without the complexities of a centralized controller. This mode allows for immediate management of each device individually, making it an ideal choice for smaller networks, such as home setups or small offices.
In Standalone Mode, each device operates independently, which simplifies the management process. Users can quickly configure basic settings without the need for extensive technical knowledge. This mode is particularly beneficial for networks with a limited number of EAPs or routers, where advanced features and centralized control are not necessary.
Exploring Controller Mode
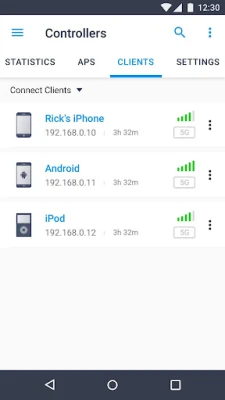
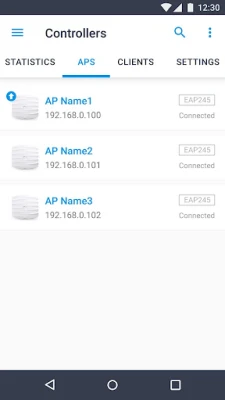
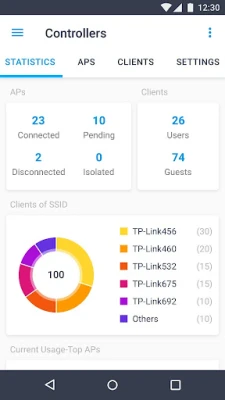
In contrast, Controller Mode is designed for more extensive network environments that require centralized management of multiple devices, including gateways, switches, and EAPs. This mode operates in conjunction with either a software Omada Controller or a hardware Cloud Controller, providing a comprehensive solution for network administrators.
One of the standout features of Controller Mode is its ability to configure and synchronize settings across all devices in the network automatically. This capability not only streamlines the management process but also ensures consistency in configurations, which is vital for maintaining network integrity.
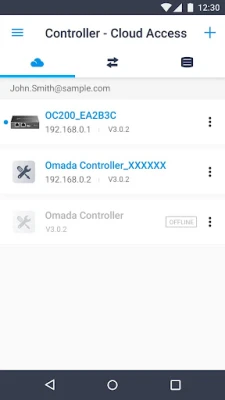
Accessing Controller Mode
Controller Mode offers two primary access methods: Local Access and Cloud Access.
- Local Access: This mode allows the Omada app to manage devices when both the Controller and the mobile device are on the same subnet. It is ideal for on-site management, providing quick access to device settings and configurations.
- Cloud Access: With Cloud Access, users can manage their devices remotely via the internet. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for network administrators who need to oversee multiple locations or require access while on the go.
Compatibility and Supported Devices
For optimal performance in Controller Mode, compatibility with specific hardware and software is essential. The current supported hardware includes:
- Hardware Cloud Controllers: OC200 V1, OC300 V1
- Software Omada Controller: Version 3.0.2 and above
To ensure a seamless experience and access to the latest features, it is recommended to upgrade to the latest version of the controller software.
Devices Supported in Standalone Mode
Standalone Mode supports a variety of models, provided they are running the latest firmware. The compatible devices include:
- EAP245 (EU)/(US) V1
- EAP225 (EU)/(US) V3/V2/V1
- EAP115 (EU)/(US) V4/V2/V1
- EAP110 (EU)/(US) V4/V2/V1
- EAP225-Outdoor (EU)/(US) V1
- EAP110-Outdoor (EU)/(US) V3/V1
- EAP115-Wall (EU) V1
- EAP225-Wall (EU) V2
- ER706W (EU)/(US) V1/V1.6
- ER706W-4G (EU)/(US) V1/V1.6
For the latest firmware updates, users can visit the official TP-Link website at TP-Link Omada Compatibility List.
Conclusion
Choosing between Standalone Mode and Controller Mode depends largely on the size and complexity of your network. For smaller setups, Standalone Mode offers simplicity and ease of use, while Controller Mode provides the robust management capabilities needed for larger, more intricate networks. Understanding these modes and their compatibility with various devices will empower users to make informed decisions, ensuring optimal network performance and management.
As technology continues to evolve, more devices will be supported by the Omada app, enhancing the user experience and expanding management capabilities. Stay updated with the latest advancements to maximize your network's potential.
Rate the App
User Reviews
Popular Apps









Editor's Choice