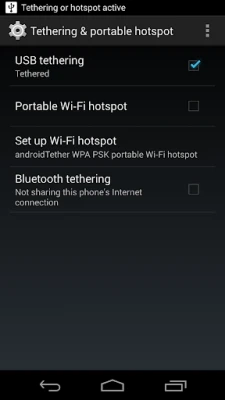
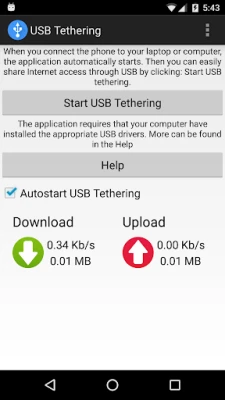
Latest Version
October 31, 2025
Duck Software
Communication
Android
1
Free
com.usb_tethering
Report a Problem
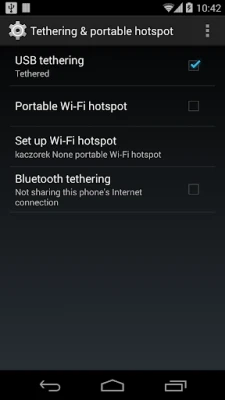
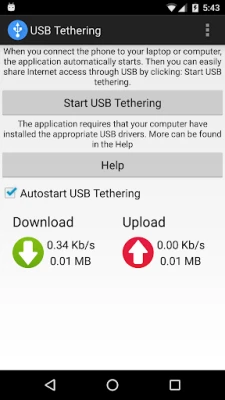
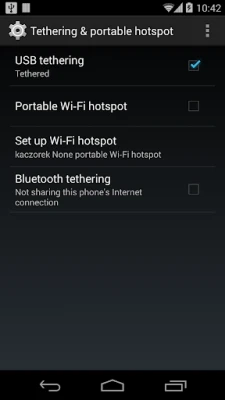
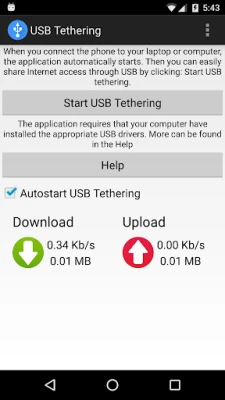
More About USB Tethering
Comprehensive Testing of Applications on Android Versions 4.0 to 6.0
In the rapidly evolving world of mobile technology, ensuring that applications function seamlessly across various operating systems is crucial. This article delves into the extensive testing of applications on Android versions 4.0 to 6.0, highlighting the significance of compatibility, performance, and user experience.
Understanding Android Versions 4.0 to 6.0
Android 4.0, also known as Ice Cream Sandwich, marked a significant milestone in the Android ecosystem. It introduced a refined user interface and enhanced functionality, setting the stage for subsequent versions. Android 4.1 to 4.3 (Jelly Bean) further improved performance and user experience, while Android 5.0 (Lollipop) brought a complete redesign and new features. Finally, Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) focused on optimizing battery life and enhancing security.
The Importance of Application Testing
Testing applications across different Android versions is essential for several reasons:
- Compatibility: Ensuring that an application runs smoothly on various Android versions helps reach a broader audience.
- Performance: Identifying performance issues early can prevent negative user experiences and improve app ratings.
- User Experience: A well-tested application provides a consistent and enjoyable experience, which is vital for user retention.
Testing Methodologies for Android Applications
To achieve comprehensive testing, several methodologies can be employed:
1. Manual Testing
Manual testing involves human testers interacting with the application to identify bugs and usability issues. This method allows for a nuanced understanding of user experience across different Android versions.
2. Automated Testing
Automated testing utilizes scripts and tools to execute test cases. This approach is efficient for regression testing and can quickly identify issues across multiple Android versions.
3. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing focuses on ensuring that the application functions correctly on various devices and Android versions. This includes testing on different screen sizes, resolutions, and hardware specifications.
Key Features to Test Across Android Versions
When testing applications on Android versions 4.0 to 6.0, several key features should be prioritized:
1. User Interface (UI) Consistency
Different Android versions may render UI elements differently. Testing should ensure that the application maintains a consistent look and feel across all targeted versions.
2. Performance Metrics
Monitoring performance metrics such as load times, responsiveness, and memory usage is crucial. Applications should perform optimally, regardless of the Android version.
3. Security Features
With each Android update, security features evolve. Testing should verify that the application adheres to the latest security protocols and protects user data effectively.
Challenges in Testing Across Multiple Android Versions
Testing applications on Android versions 4.0 to 6.0 presents unique challenges:
- Diverse Device Ecosystem: The vast array of devices running different Android versions can lead to inconsistencies in performance and user experience.
- Fragmentation: Android's fragmentation means that not all users will have access to the latest features, making it essential to test for backward compatibility.
- Resource Limitations: Older devices may have limited resources, affecting how applications perform and necessitating optimization.
Best Practices for Effective Testing
To ensure successful application testing across Android versions 4.0 to 6.0, consider the following best practices:
1. Create a Comprehensive Test Plan
A well-structured test plan should outline the testing scope, methodologies, and specific features to be tested. This ensures thorough coverage and minimizes oversight.
2. Utilize Real Devices and Emulators
Testing on real devices provides the most accurate results, while emulators can help simulate various environments. A combination of both is ideal for comprehensive testing.
3. Gather User Feedback
Incorporating user feedback during the testing phase can provide valuable insights into potential issues and areas for improvement, enhancing the overall user experience.
Conclusion
Thorough testing of applications on Android versions 4.0 to 6.0 is vital for ensuring compatibility, performance, and user satisfaction. By employing effective testing methodologies and adhering to best practices, developers can create robust applications that cater to a diverse user base. As the Android ecosystem continues to evolve, staying vigilant in testing will remain a cornerstone of successful application development.
Rate the App
User Reviews
Popular Apps









Editor's Choice