Latest Version
4.0.3
October 10, 2025
iCivics
Games
Android
0
Free
air.com.filament.argumentwars
Report a Problem
More About Argument Wars
Exploring Landmark Supreme Court Cases: A Comprehensive Guide
The United States Supreme Court has played a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s legal landscape through landmark decisions. This article delves into significant cases that have influenced American law and society, providing insights into their arguments, outcomes, and lasting impacts. Whether you are a student, educator, or simply interested in the judicial system, understanding these cases is essential.
1. Bond v. United States
In Bond v. United States, the Supreme Court addressed the issue of whether a federal law could be applied to a local crime. The case involved a woman who used a toxic chemical to harm her husband’s mistress. The Court ruled that the federal government overstepped its authority, emphasizing the importance of state sovereignty in criminal matters. This decision reinforced the principle that federal laws should not encroach upon state jurisdiction without clear justification.
2. Brown v. Board of Education
Brown v. Board of Education is perhaps one of the most significant Supreme Court cases in American history. Decided in 1954, it declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional. The Court's unanimous decision overturned the precedent set by Plessy v. Ferguson, which upheld the "separate but equal" doctrine. This landmark ruling not only transformed the educational landscape but also served as a catalyst for the Civil Rights Movement, promoting equality and justice for all.
3. Gideon v. Wainwright
In Gideon v. Wainwright, the Supreme Court ruled that the Sixth Amendment guarantees the right to counsel for defendants in criminal cases, even if they cannot afford an attorney. This 1963 decision underscored the principle of fair trial rights and ensured that justice is accessible to all individuals, regardless of their financial status. The ruling has had a profound impact on the American legal system, reinforcing the idea that legal representation is a fundamental right.
4. Hazelwood v. Kuhlmeier
The case of Hazelwood v. Kuhlmeier addressed the issue of student free speech in public schools. In 1988, the Supreme Court ruled that school administrators could exercise editorial control over school-sponsored publications. This decision highlighted the balance between students' rights and the educational institution's responsibility to maintain an appropriate learning environment. It remains a critical case in discussions about student expression and administrative authority.
5. In Re Gault
In Re Gault was a landmark case that established the rights of juveniles in the legal system. The Supreme Court ruled that minors have the right to due process, including the right to legal counsel and the right to confront witnesses. This 1967 decision marked a significant shift in how the justice system treats young offenders, ensuring that they receive fair treatment and protection under the law.
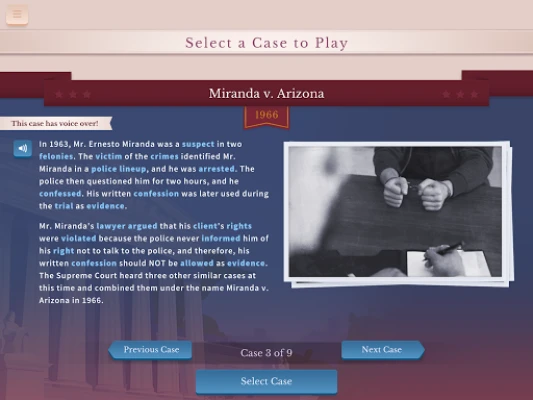
6. Miranda v. Arizona
In Miranda v. Arizona, the Supreme Court established the requirement for law enforcement to inform individuals of their rights upon arrest, including the right to remain silent and the right to an attorney. This 1966 ruling aimed to protect individuals from self-incrimination and ensure that confessions are made voluntarily. The "Miranda warning" has since become a fundamental aspect of police procedure in the United States.
7. New Jersey v. T.L.O.
The case of New Jersey v. T.L.O. addressed the issue of search and seizure in public schools. The Supreme Court ruled that school officials could search a student’s belongings if they have reasonable suspicion of wrongdoing. This 1985 decision balanced students' rights to privacy with the need for school safety, establishing guidelines for searches conducted by school authorities.
8. Snyder v. Phelps
Snyder v. Phelps involved the controversial issue of free speech and protest. The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the Westboro Baptist Church, which had protested at the funeral of a U.S. Marine. The Court held that the First Amendment protects even offensive speech, emphasizing the importance of free expression in a democratic society. This decision sparked debates about the limits of free speech and the rights of individuals to protest.
9. Texas v. Johnson
In Texas v. Johnson, the Supreme Court ruled that burning the American flag is a form of symbolic speech protected by the First Amendment. This 1989 decision reaffirmed the principle that freedom of expression includes actions that may be deemed offensive or disrespectful. The ruling has had lasting implications for discussions about patriotism, protest, and the boundaries of free speech.
Conclusion: The Significance of Supreme Court Precedents
Understanding these landmark Supreme Court cases is crucial for recognizing the evolving nature of American law and the Constitution's role in shaping societal norms. Each case illustrates the delicate balance between individual rights and governmental authority, highlighting the importance of judicial review in protecting civil liberties. As students and educators engage with these cases, they gain valuable insights into the legal principles that govern our society.
Resources for Educators and Students
For educators looking to enhance their teaching resources, consider exploring Argument Wars on iCivics. This interactive platform allows students to analyze arguments and outcomes of landmark Supreme Court cases, evaluate reasoning, and recognize the significance of constitutional precedents. By engaging with these resources, students will develop a deeper understanding of the judicial system and its impact on their lives.
In conclusion, the exploration of these landmark cases not only enriches our understanding of the law but also empowers individuals to engage thoughtfully in discussions about justice, rights, and the role of the Supreme Court in American democracy.
Rate the App
User Reviews
Popular Apps










Editor's Choice