Latest Version
December 29, 2025
TERA RESEARCH LAB COMPANY LIMITED
Education
Android
0
Free
com.duy.calculator.free
Report a Problem
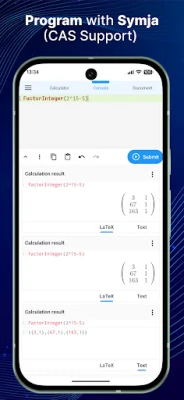
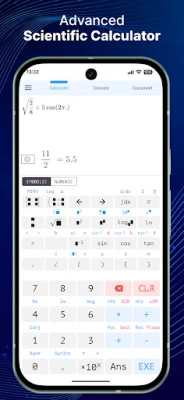
More About Calculator N+ - Math Solver
Mastering Mathematics: A Comprehensive Guide to Algebra, Calculus, Trigonometry, and More
Mathematics is a vast field that encompasses various branches, each with its unique concepts and applications. This article delves into essential mathematical topics, including algebra, calculus, trigonometry, statistics, and combinatorics. Whether you're a student, educator, or math enthusiast, understanding these concepts can enhance your problem-solving skills and analytical thinking.
Algebra: The Foundation of Mathematics
Algebra serves as the cornerstone of mathematics, providing tools to solve equations and understand relationships between variables. Here are some key areas within algebra:
1. Computer Science Functions
In computer science, functions play a crucial role in programming and algorithm design. Understanding how to define and manipulate functions is essential for developing efficient code.
2. Solving Equations
Equations are mathematical statements that assert the equality of two expressions. Mastering techniques to solve linear and quadratic equations is vital for progressing in mathematics.
3. Systems of Equations
Systems of equations involve multiple equations that share variables. Learning methods such as substitution and elimination can help find solutions to these systems.
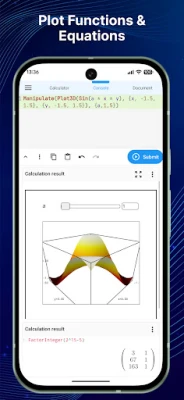
4. Graphing Functions
Graphing functions allows for visual representation of relationships between variables. Understanding how to plot graphs accurately is essential for interpreting data and functions.
5. Cartesian Geometry
Cartesian geometry, or coordinate geometry, uses a coordinate system to define geometric shapes and relationships. This branch is fundamental for understanding spatial relationships in mathematics.
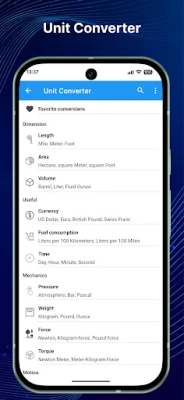
6. Unit Conversions
Unit conversions are necessary for solving real-world problems involving different measurement systems. Mastering this skill ensures accuracy in calculations.
7. Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Simplifying expressions is a critical skill in algebra. It involves reducing complex expressions to their simplest form, making calculations easier and more efficient.
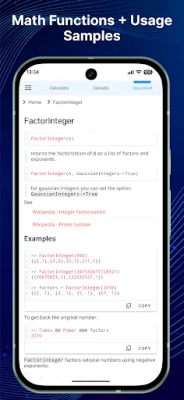
8. Polynomial Factorization
Factorization of polynomials is essential for solving polynomial equations. Understanding how to break down polynomials into their factors can simplify many mathematical problems.
9. Binomial Expansion (Newton's Formula)
Binomial expansion allows for the expansion of expressions raised to a power. Newton's formula provides a systematic way to achieve this, which is useful in various applications.
10. Matrix Calculations
Matrices are powerful tools in algebra, used for solving systems of equations and performing transformations. Mastering matrix operations is crucial for advanced mathematical studies.
Calculus: The Study of Change
Calculus is the mathematical study of continuous change, focusing on derivatives and integrals. Here are the core concepts:
1. Derivatives
Derivatives measure how a function changes as its input changes. Understanding derivatives is fundamental for analyzing rates of change in various contexts.
2. Antiderivatives
Antiderivatives, or indefinite integrals, are the reverse process of differentiation. They are essential for solving problems involving area under curves.
3. Definite Integrals
Definite integrals calculate the area under a curve between two points. This concept is crucial for applications in physics, engineering, and economics.
4. Limits of Sequences and Functions
Limits are foundational in calculus, helping to define continuity and the behavior of functions as they approach specific points. Understanding limits is essential for mastering calculus concepts.
Trigonometry: The Study of Angles
Trigonometry focuses on the relationships between angles and sides of triangles. Here are some key concepts:
1. Trigonometric Expansion
Trigonometric identities, such as sin(2x) = 2sin(x)cos(x), are essential for simplifying expressions and solving equations.
2. Trigonometric Reduction
Trigonometric reduction involves transforming complex expressions into simpler forms, such as converting 2sin(x)cos(x) back to sin(2x).
3. Exponential Form of Trigonometric Functions
Converting trigonometric and hyperbolic functions to exponential form simplifies calculations and provides deeper insights into their properties.
Statistics & Combinatorics: Analyzing Data
Statistics and combinatorics are essential for analyzing data and understanding probability. Key concepts include:
1. Combinations
Combinations refer to the selection of items from a larger set, where the order does not matter. This concept is crucial in probability and statistics.
2. Permutations
Permutations involve arranging items in a specific order. Understanding permutations is vital for solving problems related to arrangements and sequences.
Additional Mathematical Features
Beyond the core topics, several additional features enhance mathematical understanding:
1. Prime Factorization
Prime factorization involves breaking down numbers into their prime components, which is essential for various mathematical applications.
2. Modulo Calculations
Modulo calculations are used in number theory and computer science, helping to determine remainders in division.
3. Catalan Numbers
Catalan numbers are a sequence of natural numbers with applications in combinatorial mathematics, particularly in counting problems.
4. Fibonacci Numbers
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. This sequence appears in various natural phenomena and mathematical contexts.
Calculator Modes: Decimal and Fraction
The calculator supports two computation modes:
- Decimal Mode: Provides results in decimal form, e.g., 0.12312312323.
- Fraction Mode: Offers precise symbolic results, e.g., 999999.
This combination of
Rate the App
User Reviews
Popular Apps









Editor's Choice