Latest Version
January 20, 2026
Taiijas Infotech
Education
Android
0
Free
com.taiijas.php_mysql
Report a Problem
More About PHP MySQL tutorial
Mastering PHP: A Comprehensive Guide to Dynamic Web Development
PHP, a powerful server-side scripting language, is essential for creating dynamic and interactive web pages. As a widely-used and free alternative to competitors like Microsoft's ASP, PHP has become a cornerstone of web development. This article will guide you through the essentials of learning PHP quickly and effectively, particularly for beginners interested in web applications.
Learn PHP in Just 5 Days
If you're eager to dive into the world of PHP, our crash course on PHP and MySQL is designed to help you learn the fundamentals in just five days. This user-friendly application allows you to grasp PHP concepts swiftly, making it an ideal choice for beginners.
Download and Install the PHP & MySQL App
The PHP & MySQL app is available for download and does not require an internet connection for its core functionalities, aside from occasional ads. With over 100,000 downloads, this app has garnered significant support from learners worldwide. For those seeking an ad-free experience, an alternative version is available at the following link: Download PHP & MySQL App.
Setting Up PHP and MySQL on Your System
To start running PHP scripts, you need to install PHP and MySQL on your system. Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing PHP on Windows using WAMP Server:
Step 1: Download WAMP Server
Visit the official WAMP Server website at www.wampserver.com to download the installation file.
Step 2: Install WAMP Server
Run the downloaded installation file and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
Step 3: Start WAMP Server Services
Once installed, launch WAMP Server and start all the necessary services. You should see a green icon in the system tray, indicating that the server is running smoothly.
Verifying Your PHP Installation
After installing PHP, it’s crucial to verify that the installation was successful. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Place Your Scripts in the www Folder
To run PHP scripts, you must place them in the 'www' folder of the WAMP directory. If your scripts are not in this folder, they will not execute.
Step 2: Open Your Web Browser
Launch your preferred web browser and type http://localhost in the address bar. If the WAMP Server home page appears, your installation is successful. If not, you may need to troubleshoot the installation process.
Running Your First PHP Script
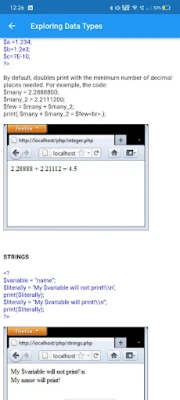
To execute a PHP script, save your file with a .php extension in the 'www' directory. You can create your own folder within this directory to organize your scripts. To run your script directly, simply enter the file name after 'localhost'. For example, if your file is named first.php, you would type http://localhost/first.php in your browser's URL bar to run it without needing a separate folder.
Conclusion
Learning PHP and MySQL opens up a world of possibilities for web development. With the right tools and resources, you can quickly become proficient in creating dynamic web applications. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to mastering PHP in no time. Embrace the journey of web development, and enjoy the process of creating interactive and engaging web pages!
Rate the App
User Reviews
Popular Apps









Editor's Choice